Invention, Intellectual Property, and Income
This week is all about understanding of copyrights and patents. Also we have to understand about intellectual property and income. In lecture Neil took brief lecture on all these terms.
Individual Assignment: Develop a plan for dissemination of your final project. prepare drafts of your summary slide and video clip and put them in your root directory
Invention:
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition or process. The invention process is a process within an overall engineering and product development process. It may be an improvement upon a machine or product or a new process for creating an object or a result. An invention that achieves a completely unique function or result may be a radical breakthrough. Such works are novel and not obvious to others skilled in the same field. An inventor may be taking a big step toward success or failure.
Some inventions can be patented. A patent legally protects the intellectual property rights of the inventor and legally recognizes that a claimed invention is actually an invention.The rules and requirements for patenting an invention vary by country and the process of obtaining a patent is often expensive.
Intellectual Property:
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect.There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The most well-known types are copyrights, patents, trademarks, and trade secrets.Intellectual property rights include patents, copyright,
industrial design rights, trademarks, plant variety rights, trade dress, geographical indications,and in some jurisdictions trade secrets. There are also more
specialized or derived varieties of generics exclusive rights, such as circuit design rights , supplementary protection certificates for pharmaceutical products , and database rights.
The term "industrial property" is sometimes used to refer to a large subset of intellectual property rights including patents, trademarks, industrial designs,utility models, service marks, trade names, and geographical indications.
There are 5 types of intellectual property, which I described one by one below:
1)Patents
2) Trademarks
3) Trade dress
4) Trade secret
5) Copyrights
Patents:
A patent is a form of right granted by the government to an inventor or their successor-in-title, giving the owner the right to exclude others from making, using, selling, offering to sell,and importing an invention for a limited period of time, in exchange for the public disclosure of the invention. An invention is a solution to a specific technological problem, which may be a product or a process and generally has to fulfill three main requirements:it has to be new, not obvious and there needs to be an industrial applicability. To enrich the body of knowledge and stimulate innovation, it is an obligation for patent owners to disclose valuable information about their inventions to the public.
Trademarks:
A trademark is a recognizable sign, design or expression which distinguishes products or services of a particular trader from similar products or services of other traders.
Trade dress:
Trade dress is a legal term of art that generally refers to characteristics of the visual and aesthetic appearance of a product or its packaging (or even the design of a building) that signify the source of the product to consumers.
Trade secrets:
A trade secret is a formula, practice, process, design, instrument, pattern, or compilation of information which is not generally known or reasonably ascertainable, by which a business can obtain an economic advantage over competitors and customers. There is no formal government protection granted; each business must take measures to guard its own trade secrets.
Copyright:
A copyright gives the creator of an original work exclusive rights to it, usually for a limited time. Copyright may apply to a wide range of creative, intellectual, or artistic forms, or "works".Copyright does not cover ideas and information themselves, only the form or manner in which they are expressed.
There are many types of copyrights:
Creative Commons (CC) License:
Open source license is that allows the source code or design to be used, shared or modified under defined terms and conditions. Open-source licensed product is mostly free of cost.The most common open source licenses available are MIT license, Apache license and GNU GPLv3 license.a. MIT license:- The MIT License is a permissive license that is short and to the point.Licensed works, modifications, and larger works may be distributed under different terms and without source code.
BSD Berkeley Software Distribution:
It is a family of permissive free software licenses, imposing minimal restrictions on the use and redistribution of covered software.
The MIT License:
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software,and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do.
Apache License:
The Apache Software Foundation uses various licenses to distribute software and documentation, to accept regular contributions from individuals and corporations, and to accept larger grants of existing software products.
I went through all the information which I mentioned and try to understand which one is useful for me.Finally I decided to go with creative commons open source license.
Creative Commons License:
All Creative Commons licenses have many important features in common.Every license helps creators — we call them licensors if they use our tools —retain copyright while allowing others to copy, distribute, and make some uses of their work — at least non-commercially. Every Creative Commons license also ensures licensors get the credit for their work they deserve.
Attribution(CC BY):
This license lets others distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon your work, even commercially, as long as they credit you for the original creation.This is the most accommodating of licenses offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials.
Attribution-ShareAlike(CC BY-SA):
This license lets others remix, adapt, and build upon your work even for commercial purposes, as long as they credit you and license their new creations under the identical terms. This license is often compared to “copyleft” free and open source software licenses. All new works based on yours will carry the same license, so any derivatives will also allow commercial use.
Attribution-NoDerivs(CC BY-ND):
This license lets others reuse the work for any purpose, including commercially; however, it cannot be shared with others in adapted form, and credit must be provided to you.
Attribution-NonCommercial(CC BY-NC):
This license lets others remix, adapt, and build upon your work non-commercially, and although their new works must also acknowledge you and be non-commercial,they don’t have to license their derivative works on the same terms.
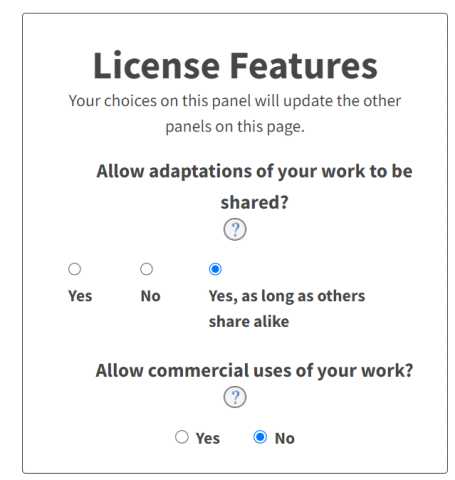
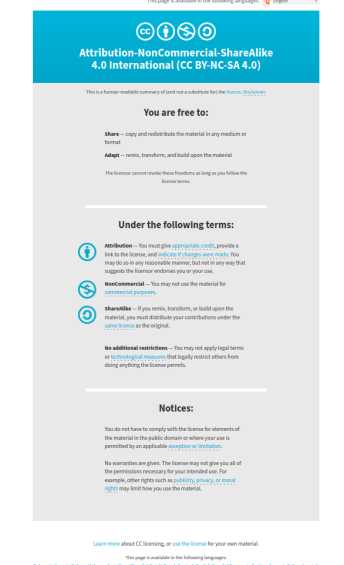
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike(CC BY-NC-SA):
This license lets others remix, adapt, and build upon your work non-commercially,
as long as they credit you and license their new creations under the identical terms.
I decide to create a license for my project using Creative Commons.
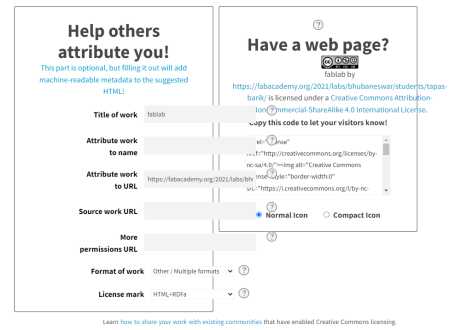
License for my work

fablab by https://fabacademy.org/2021/labs/bhubaneswar/students/tapas-barik/ is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
summary slide
video clip
2) Trademarks
3) Trade dress
4) Trade secret
5) Copyrights
as long as they credit you and license their new creations under the identical terms.

fablab by https://fabacademy.org/2021/labs/bhubaneswar/students/tapas-barik/ is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.